Reproduction and Modification in Plants | Term 1 Unit 5 | 7th Science - Student Activities | 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 5 : Reproduction and Modification in Plants
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 5 : Reproduction and Modification in Plants
Student Activities
ACTIVITY 1
Aim:
To raise a new generation of plant from watermelon and potato.
Materials required:
Two pots with soil, potato, watermelon seeds and water.
Procedure:
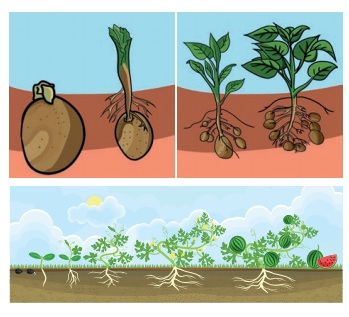
Fill both pots with soil mixed with compost or manure. Take young potato. Ensure that it is not dried up and the skin still looks fresh. Bury a potato in one part. Sow watermelon seeds in another pot. Pour water regularly and maintain the plant
Observation:
After few days, we can see single plant arising from a buried potato. Plants arise from the pot sowed with watermelon seeds. Each seed produces a plant
Inference:
Watermelon plants were produced from seeds. Potato plant is not from seed, but from the stem tuber (vegetative part). Seed is not only the source for new generation, even vegetative part of a plant can also be used to produce a new plant.
ACTIVITY 2
Take a flower. Dissect as shown longitudinally and find parts inside the flower. Can you identify the male reproductive part, androecium (stamen, filament and pollen sac). Carefully observe the female reproductive part, gynoecium (ovary, style and stigma). If they are not seen clearly, gently pluck off the sepals and petals. Make a drawing of the parts and arrangement in your notebook.
ACTIVITY 3
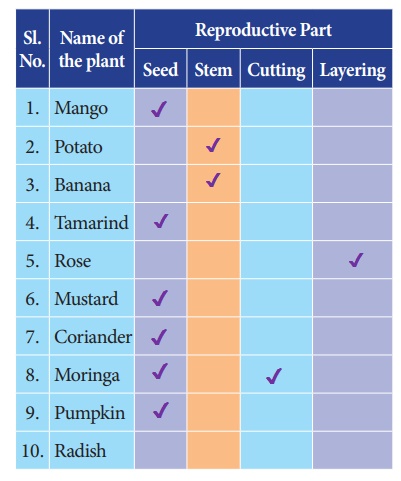
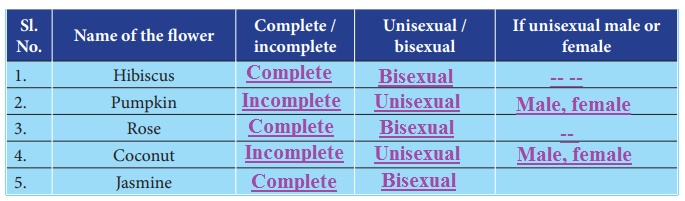
Using the information from the above complete the following table:
The sunflower is not asingle flower. It is a group of flowers clustered together. A group of flowers arranged together is called inflorescence. Tridax procumbens, looks like a single flower, but is an inflorescence. Leaf juice of this plant is used to cure wounds and cuts.
ACTIVITY 4
Make a flower album
Press the collected flowers between pages of newspaper or book. Place two thick sheets and keep a heavy object, such as brick, on the top to apply pressure. Turn the sides every two to three days. Allow flowers to dry completely. Collect the dried flowers and paste them in an album. Now, your flower album ready.
1. The world’s largest and heaviest seed is the double coconut. The seed looks liketwo coconut fused together. It only grows in two islands of the Seychelles. A single seed may be 12 inches long, nearly 3 feet in circumference and weighs about 18 kg.
2. Orchids have the smallest seeds in the plant kingdom. 35 million seeds may weight only about 25 gram.
ACTIVITY 5
Aim: To study the modification of root.
Materials Required: Sample / charts of raddish, carrot, beet root, sweet potato, stilt roots and pneumatophores.
Procedure: Carefully observe the shape of each specimen.
Observation: Draw the diagram and observe the morphological differences between the samples.
ACTIVITY 6
Aim: To study the modification of stem Materials Required: Specimens of Ginger, Potato, Onion, Mint, Bougainvillea–, Acacia, Opuntia and locally available specimens.
Procedure: Observe the external morphology of each specimen.
Observation: Draw diagram and bring out the differences and their function in each type of stem modifications.
Related Topics