Book Back Important Questions Answers | Choose the Correct Answers | Short, brief Answers | Zoology - Reproduction in Organisms: Questions and Answers (Evaluation) | 12th Zoology : Chapter 1 : Reproduction in Organisms
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 1 : Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction in Organisms: Questions and Answers (Evaluation)
Evaluation
1. In which type of parthenogenesis are only males produced?
a) Arrhenotoky
b) Thelytoky
c) Amphitoky
d) Both a and b
Answer: a. Arrhenotoky
2. Animals giving birth to young ones:
a) Oviparous
b) Oviviviparous
c) Viviparous
d) Both a and b
Answer: c. Viviparous
3. The mode of reproduction in bacteria is by
a) Formation of gametes
b) Endospore formation
c) Conjugation
d) Zoospore formation
Answer: c.
Conjugation
4. In which mode of reproduction variations are seen
a) Asexual
b) Parthenogenesis
c) Sexual
d) Both a and b
Answer: c. Sexual
5. Assertion and reasoning questions:
In each of the following questions there are two statements. One is assertion (A) and other is reasoning (R). Mark the correct answer as
A. If both A and R are true and R is correct explanation for A
B If both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation for A
C. If A is true but R is false
D. If both A and R are false.
I. Assertion: In bee society, all the members are diploid except drones.
Reason: Drones are produced by parthenogenesis.
A B C D
II. Assertion: Offsprings produced by asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent.
Reason: Asexual reproduction involves only mitosis and no meiosis.
A B C D
III. Assertion: Viviparous animals give better protection to their offsprings.
Reason: They lay their eggs in the safe places of the environment.
A B C D Answer: C
6. Name an organism where cell division is itself a mode of reproduction.
Amoeba reproduces by fission, that is by cell division
itself a mode of reproduction.
7. Name the phenomenon where the female gamete directly develops into a new organism with an avian example.
The phenomenon is Parthenogenesis. Turkey is the bird
in which the female gamete directly develops into a new organism.
8. What is parthenogenesis? Give two examples from animals
• The egg develops into a complete individual without fertilization is known
as parthenogenesis.
• Example : Rotifers,
Honeybees and Turkey
9. Which type of reproduction is effective -Asexual or sexual and why?
• Sexual reproduction is more effective than asexual reproduction.
• In asexual reproduction there is no variation.
• In sexual reproduction due to fusion of two gametes, variation is found.
10. The unicellular organisms which reproduce by binary fission are considered immortal. Justify.
• Amoeba is an unicellular organism, which is considered as immortal.
• The parental amoeba mitotically divides into two daughter amoebae.
11. Why is the offspring formed by asexual reproduction referred as a clone?
• The offsprings formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to
the parent.
• They can also be referred as a clone.
• Clone is the exact copy of an organism which it is developed.
12. Why are the offsprings of oviparous animal at a greater risk as compared to offsprings of viviparous organisms?
• The offsprings of the viviparous organism develops within the female.
• The offsprings of the oviparous organisms develops in the external
environment.
• There are certain external environment factors that affects the
development of the offsprings.
• Hence offsprings of the oviparous animals are at greater risk.
13. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Some organisms like honey bees are called parthenogenetic animals
(b) A male honey bee has 16 chromosomes where as its female has 32 chromosomes.
a) Organisms like
honey bees can reproduce without fertilization.
b) • Male honey bees are formed without fertilization (ie) Egg alone.
• Female honey bees are formed fertilization (ie) Fusion of male and female
gamete.
• That is why male has 16 chromosomes in the egg
• The female are diploid having 32 chromosomes, 16 from male and 16 from
female.
14. Differentiate between the following:
(a) Binary fission in amoeba and multiple fission in Plasmodium
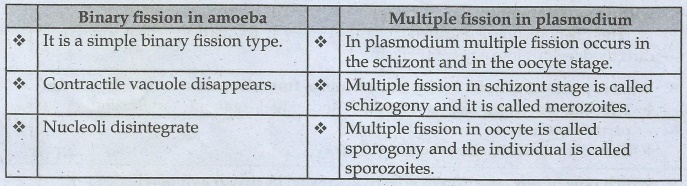
Binary fission in amoeba
• It is a simple binary fission type.
• Contractile vacuole disappears.
• Nucleoli disintegrate
Multiple fission in plasmodium
• In plasmodium multiple fission occurs in the schizont and in the oocyte
stage.
• Multiple fission in schizont stage is called schizogony and it is called
merozoites.
• Multiple fission in oocyte is called sporogony and the individual is
called sporozoites.
(b) Budding in yeast and budding in Hydra
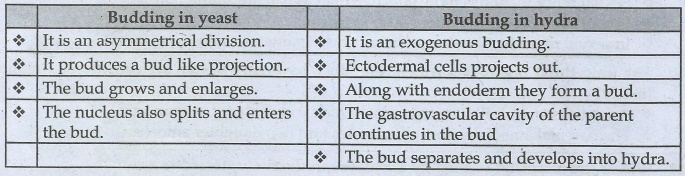
Budding in yeast
• It
is an asymmetrical division.
• It
produces a bud like projection.
• The
bud grows and enlarges.
• The
nucleus also splits and enters the bud.
Budding in hydra
• It
is an exogenous budding.
• Ectodermal
cells projects out.
• Along
with endoderm they form a bud.
• The
gastrovascular cavity of the parent continues in the bud
• The
bud separates and develops into hydra.
(c) Regeneration in lizard and Planaria
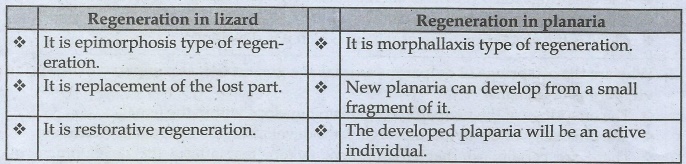
Regeneration in lizard
• It
is epimorphosis type of regeneration.
• It
is replacement of the lost part.
• It
is restorative regeneration.
Regeneration in planaria
• It
is morphallaxis type of regeneration.
• New
planaria can develop from a small fragment of it.
• The
developed plaparia will be an active individual.
15. How is juvenile phase different from reproductive phase?
Juvenile Phase:
• It is the period of growth between the birth of the individual upto
reproductive maturity.
• The juvenile stage of certain organisms
Insects - Larva
Cow - Calf
Ape - Infant
Cat - Kitten
Reproductive Phase :
• The period in which the organisms are able to reproduce.
• Each organism's breeding time differs.
• If they reproduce at the particular period of the year it is called
seasonal breeders.
(Eg.) Birds.
• If they are able to reproduce throughout their sexual maturity it is known
as continuous breeders. (Eg.) Poultry and Rabbit.
16. What is the difference between syngamy and fertilization?

Syngamy
• It is the fusion of male and female pronuclei after fertilization.
• It confirms the diploid state of the zygote.
Fertilization
• It is the fusion of male and female gamete.
• It refers to the process of confirming fertility.
Related Topics