Development of Industries in India | Chapter 6 | History | 8th Social Science - Questions with Answers | 8th Social Science : History : Chapter 6 : Development of Industries in India
Chapter: 8th Social Science : History : Chapter 6 : Development of Industries in India
Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
answer
1. Which
of the following activities of the people will not come under handicraft?
a. Carving statues out of stone
b. Making bangles with glass
c. Weaving silk sarees
d. Smelting of iron
[Answer:
d) Smelting of iron]
2. The oldest industry in India was industry.
a. Textile
b. Steel
c. Electrical
d. Fertilizers
[Answer:
a) Textile]
3. The woollen and leather factories became prominent in
a. Bombay
b. Ahmadabad
c. Kanpur
d. Dacca
[Answer:
c) Kanpur]
4. What was the aim of first Three Five year Plans of India?
a. To control population growth
b. To reduce illiteracy rate
c. To built a strong industrial base
d. To empower the women
[Answer:
c) To built a strong industrial base]
5. What was not the reason for the decline of Indian
Industries?
a. Loss of royal patronage
b. Competition of machine made goods
c. Industrial policy of India
d. Trading policy of British
[Answer:
c) Industrial policy of India]
II Fill in the blanks
1. Craft
was the integral part in the life of
the people.
2. Industrial revolution took place in
England.
3. The Assam Tea Company was founded
in 1839.
4. Jute industry was started in the
Hoogly Valley at Rishra
near Calcutta.
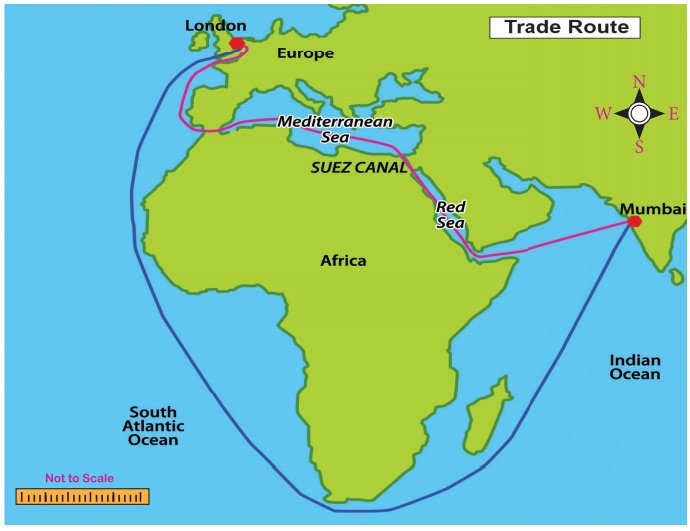
5. Suez Canal shortened the distance between Europe and India.
III Match the
following
1. Tavernier - Drain Theory
2. Dacca - Paper mill
3. Dadabai Naoroji - Artisan
4. Ballygunj - Muslin
5. Smiths - French traveler
Answer:
1.
Thvernier – French traveller
2. Dacca
- Muslin
3.
Dadabai Naoroji - Drain Theory
4.
Ballygunj – Paper mill
5.
Smiths- Artisan
IV State True or False
1. India was famous for cotton and
silk cloths. [Answer: True]
2. The railway was introduced in
India by the British. [Answer: True]
3. Steel was first manufactured by
modern methods at Jamshedpur. [Answer: False]
Correct
statement: Steel was first
manufactured by modern methods at Kulti
in 1874.
4. The industrial policy of 1948,
brought mixed economy in industrial sector. [Answer: True]
5. The tenth and eleventh five year
plans witnessed a high growth rate of Agricultural production. [Answer: False]
Correct
statement: The Tenth and Eleventh Five-Year
Plans witnessed a high growth rate of industrial
production.
V Consider the
following the statements and tick (✓) the appropriate answer
1. Which of the following statements
are correct?
i. According to Edward Baines, ‘The
birth place of cotton manufacture is in England’.
ii. Before mechanised industry
handicrafts was the second largest source of employment in rural India.
iii. Saurashtra was known for tin
industry.
iv. Construction of Suez Canal made
the
British goods cheaper in India.
a. i and ii are correct
b. ii and iv are correct
c. iii and iv are correct
d. i, ii and iii are correct
[Answer:
b) ii and iv are correct]
2.Assertion (A): Indian handicrafts collapsed under the colonial rule.
Reason (R) : British made India as the producer of raw materials and
markets for their finished products.
a. A is correct R is correct
explanation of A
b. A is correct and R is not the
correct explanation of A
c. Both A and R is correct
d. Both A and R is wrong
[Answer:
a) A is correct R is correct explanation of A]
3. Which one of the following is
wrongly matched?
a. Bernier - Shajahan
b. Cotton mill - Ahmadabad
c. TISCO - Jamshedpur
d. Economic Liberalisation – 1980
[Answer:
d) Economic Liberalisation - 1980]
VI Answer the
following in one or two sentences
1. What
are the traditional handicrafts industries of India?
Answer: (i) The traditional handicrafts industries of India are
textiles, woodwork, ivory, stone cutting, leather, fragrance wood, metal work
and jewellery.
(ii) The village artisans such as potters, weavers, smiths
produced articles and utensils.
2. Write about the drain theory.
Answer: The Drain theory of Dadabai Naoroji was the first to acknowledge
that the poverty of the Indian people was due to the British exploitation of
India’s resources and the drain of India’s wealth to Britain.
3. Name the inventions which made the production of textiles
on large scale.
Answer: The invention of cotton gin, flying shuttle, spinning jenny and
steam engine in England, which made the production of textiles on large scale.
4. Write a short note on Confederation of Indian Industry.
Answer:
(i) The Confederation of Indian Industry is a business
association in India.
(ii) CIT is a non-Government, not-for-profit, industry-led and
industry - managed organisation.
(iii) It was founded in 1985.
5. What is de-industrialisation?
Answer: The process of disruption of traditional Indian crafts and
decline in national income has been referred to as de-industrialisation.
VII Answer the
following in detail
1. How was the trading policy of British caused for the decline of the Indian
Industries?
Answer:
(i) All the policies implemented by the British government in
India had a deep impact on India’s indigenous industries.
(ii) Free trade policy followed by the East India Company
compelled the Indian traders to sell their goods below the market prices.
(iii) This forced many craftsmen to abandon their ancestral
handicraft talents.
(iv) East India company’s aim was to buy the maximum quantity of
Indian manufactured goods at the cheapest price and sell them to other European
countries for a huge profit.
(v) This affected the traditional Indian industry.
(vi) The British followed the policy of protective tariffs that
was much against the trading interests of India.
(vii) Heavy duties were charged on Indian goods in Britain, but
at the same time, the English goods entering India were charged only nominal
duties.
2. Write in detail about the plantation industries.
Answer:
Plantation
Industries:
(i) The plantation industry was the first to attract the
Europeans. This provide jobs on large scale.
(ii) In reality, it could meet the increasing demands for tea,
coffee and indigo by the British Society.
(iii) The Assam Tea Company was founded in 1839.
(iv) Coffee plantation also started simultaneously.
(v) As the tea plantation was the most important industry of
Eastern India, coffee plantation became the centre of activities in South
India.
(vi) The Third important plantation, which gave birth to factory
was jute.
(vii) All these Industries were controlled by many former
employees of the British
East India Company.
3. Explain Industrial development after 1991 reforms.
Answer:
(i) The year 1991 ushered a new era of the economic liberalisation.
(ii) India took major decision to improve the performance of the
industrial sector.
(iii) The Tenth and Eleventh five year plans witnessed a high
growth rate of industrial production.
(iv) The abolition of Industrial licensing, dismantling of price
controls, dilution of reservation of small scale industries.
(v) Virtual abolition of monopoly law enabled Indian industry to
flourish.
(vi) The new policy welcomes foreign investments.
VIII HOTs
1. How do handicraft products differ from machine made
products?
Answer:
Handicraft: Something you make with your own hands, especially an ornament
or decoration, is a handicraft. Instead, items made by artisans like pottery,
handwoven blankets, handmade jewellery and quilts stitched by hand are all
examples of handicrafts.
Machine
made Products : Machine made Products are
produced faster and all are exactly the same. Machine manufacturing is faster
and more economical. Also machine made goods are cheaper than hand made goods.
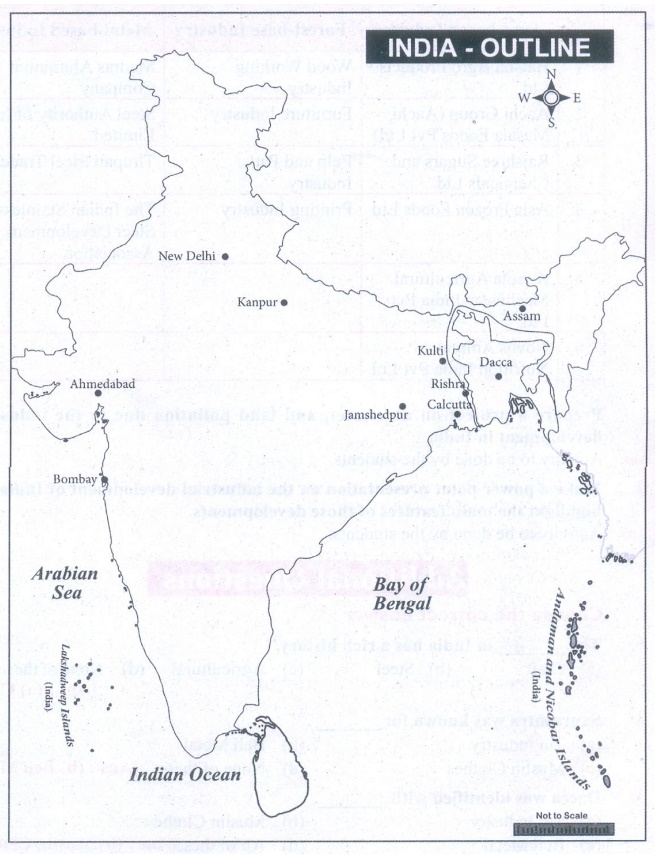
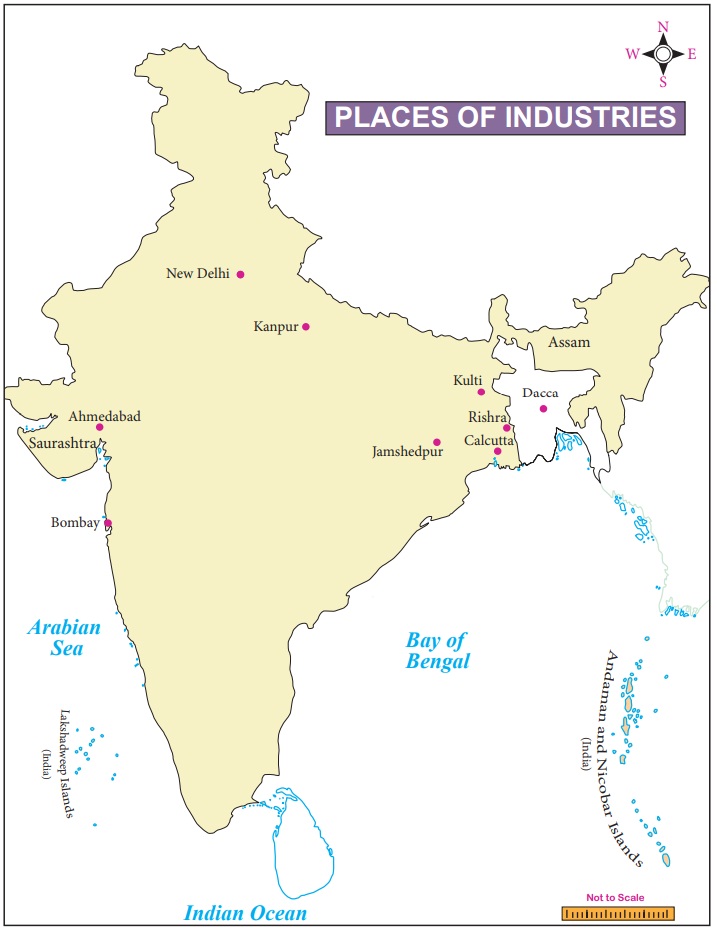
IX Mark the following
places on the outline map of India
1. Bombay
2. Calcutta
3. Dacca
4. Jamshedpur
5. Rishra
6. Ahmadabad
7. Kanpur
8. Kulti
9. New Delhi
10 Assam
X Project and
Activity
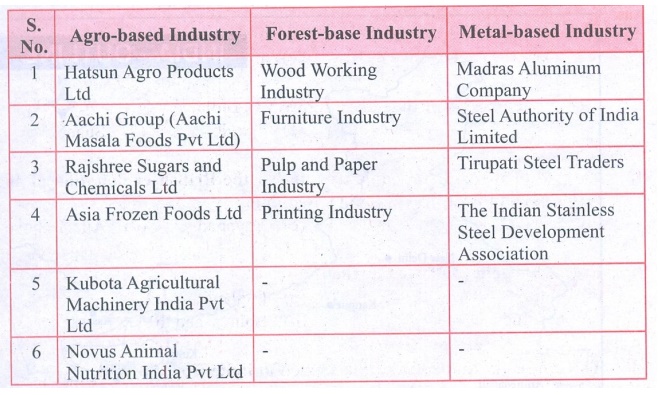
1. Name the industries in your state and divide them into
Agro based metal based and forest based.
2. Prepare a project on air, water, and land pollution due to the industrial development in India.
3. Make a power point presentation on the industrial development of India and highlight the main features of those developments.
Related Topics