Tax and its Importance | Term 3 Unit 1 | Economics | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : Economics : Term 3 Unit 1 : Tax and its Importance
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Economics : Term 3 Unit 1 : Tax and its Importance
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose
the correct answer:
1. Taxes
are________________ payment.
a.
Voluntary
b.
Compulsory
c.
a & b
d.
None of the above
[Answer: (b)
Compulsory]
2. Minimum possible
amount should be spent in the collection of taxes is
a.
canon of equality
b.
canon of certainity
c.
canon of economy
d.
canon of convenience
[Answer: (c) canon
of economy]
3. This taxation is a
very opposite of progressive taxation.
a.
Degressive
b.
proportional
c.
regressive
d.
none
[Answer: (c) regressive]
4. Income tax is a
a.
direct tax b.
b.
indirect tax
c.
a & b
d.
degressive tax
[Answer: (a) direct
tax]
5. Which tax is raised
on provision of service.
a.
Wealth
b.
corporate
c.
wealth
d.
service
[Answer: (d)
service]
II. Fill
in the blanks:
1.
Taxation
is a term for when a taxing authority usually a government levies or imposes a
tax.
2.
Proportional
Taxation is the method, where the rate of tax is
same regardless size of the income.
3.
Gift tax
is paid to the Government by the recipient of gift depending on value of gift.
4.
Direct
tax burden cannot be shifted by tax payers.
5.
Indirect tax is more elastic
III. Match
the following:
1.
Principle of taxation – Direct Tax
2.
Estate tax – Goods and Service Tax
3.
Excise Tax – Adam Smith
4.
01.07.2017 – Less elastic
5.
Direct Tax – Indirect Tax
Answer:
1. Principle of
taxation - Adam Smith
2. Estate tax - Direct Tax
3. Excise Tax - Indirect Tax
4. 01.07.2017 - Goods and Service Tax
5. Direct Tax - Less elastic
IV. Odd
one out:
1.
Which one of the following is not a indirect tax?
2.
a) Service tax b) Value Added Tax (VAT) c) Estate duty d) Excise duty
[Answer: (c) Estate
duty]
V. Correct
one out :
1.
Which one of the following tax is a direct tax?
a.
Service tax
b.
Wealth tax
c.
Sales tax
d.
Progressive tax
[Answer: (b) Wealth
tax]
VI. Give
short answer:
1. Define tax.
Answer: Taxes are defined as a compulsory contribution from a person to
the government to defray the expenses incurred in the common interest of all
without reference to special benefits conferred.
2. Why taxes are
imposed?.
Answer: Everybody is obliged by law to pay taxes. Total Tax money goes
to government exchequer. Appointed government decides that how are taxes being
spent and how the budget is organized.
3. Write name of
taxation types and draw its diagram.
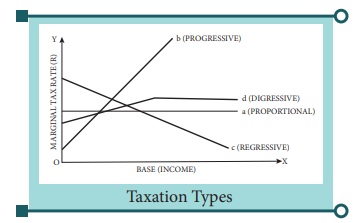
Answer: Taxation
Types:
There are four types of Taxation:
(i) Proportional Tax
(ii) Progressive Tax
(iii) Regressive Tax and
(iv) Degressive Tax
4. Write any three
importance of tax.
Answer:
(i) Health
(ii) Education
(iii) Governance
5. What are the types
of tax? and explain its.
Answer:
In modern times taxes are classified into two types. There are:
(i) Direct Tax:
A Direct tax is the tax whose burden is directly borne by the
person on whom it is imposed, (i.e), its burden cannot be shifted to others.
(ii) Indirect Tax:
When liability to pay a tax is on one person and the burden of
that tax shifts on some other person, this type of tax is called an indirect
tax.
6. Write short note on
Gift Tax and Service Tax.
Answer:
Gift Tax:
Gift tax is paid to the Government by the recipient of gift
depending on value of gift.
Service Tax:
Service tax is raised on provision of Service. This tax is
collected from the service recipients and paid to the Central Government.
7. What is Goods and
Service Tax?.
Answer:
(i) Goods and Services Tax is a kinds of tax imposed on sale,
manufacturing and usage of goods and services.
(ii) This tax is applied on services and goods at a national level
with a purpose of achieving overall economic growth.
8. Distinguish between
the direct and indirect tax.
Answer:
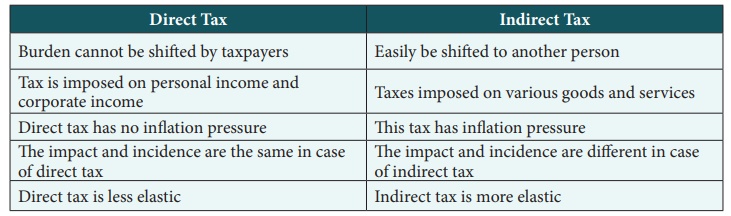
Direct Tax
1. Burden cannot be shifted by taxpayers
2. Tax is imposed on personal income and corporate income.
3. Direct tax has no inflation pressure
4. The impact and incidence are the same in case of direct tax
5. Direct tax is less elastic
Indirect Tax
1. Easily be shifted to another person
2. Taxes imposed on various goods and services
3. This tax has inflation pressure
4. The impact and incidence are different in case of indirect
tax
5. Indirect tax is more elastic
VII. Give
brief answer:
1. Write briefly about
the principles of taxation.
Answer: (i) Canon
of Equality: The government should impose taxes
in such a way that people have to pay according to their ability does not mean
equal amount of tax but it means that the burden of a tax must be fair and
just.
(ii) Canon of
Certainity: Certainty creates confidence in the
taxpayers cost of collection of taxes and increases economic welfare because it
tends to avoid all economic waste.
(iii) Canon of
Convenience: Taxes should be levied and
collected in such a manner that provides a maximum of convenience to the
taxpayers should always keep in view that the taxpayers suffer the least
inconvenience in payment of the tax.
(iv) Canon of
Economy: Minimum possible money should be spent in the
collection of taxes. Collected amount should be deposited in the Government
treasury.
2. Explain the taxation
types.
Answer: Taxation
Types:
There are four types of Taxation:
(i) Proportional Tax
(ii) Progressive Tax
(iii) Regressive Tax and
(iv) Degressive Tax
(i) Proportional
Taxation is a method, where the rate of tax is same
regardless size of the income. The tax amount realized will vary in the same
proportion as that of income. If tax rate is 5% on income, Mr. X getting an
income of Rs.1000 will pay. Rs.50, Mr. B will be getting an income Rs.5,000
will pay tax of Rs.50. In short, proportional tax leaves the relative financial
status of taxed persons unchanged.
(ii) Progressive
Taxation is a method by which the rate of tax will also
increase with the increase of income of the person a case of progressive taxation
if a person with Rs.1000 income per annum pay a tax of 10% (i.e) Rs.100, a
person with an income of Rs. 10,000 per annum pays a tax of 25% (i.e) Rs.2,500
and a person with income of 1 lakh per annum pay the tax of 50% that is
Rs.50,000.
(iii) Regressive
taxation: It implies that hire the rate of tax furrow
income groups than in the case of higher income groups it is a very opposite to
progressive taxation.
(iv) Digressive
Taxes which are to mildly progressive, hence not very
steep, so that high income earners do not make a due sacrifice on the basis of
equity, are called digressive. In digressive taxation, a tax may be progressive
up to a certain limit; after that it may be charged at a flat rate.
3. Explain the
importance of tax.
Answer: Importance
of Tax:
Taxes are crucial because governments collect this money and use
it to finance under the following social projects.
1. Health:
(i) Without taxes, government contributions to the health sector
would be impossible.
(ii) Taxes go to funding health services such as social healthcare,
medical research, social security, etc.
2. Education:
(i) Education could be one of the most deserving recipients of tax
money.
(ii) Governments put a lot of importance in the development of human
capital and education is central in this development.
3. Governance :
(i) Governance is a crucial component in the smooth running of
country affairs.
(ii) Poor governance would have far reaching ramifications on the
entire country with a heavy toll on its economic growth.
(iii) Good governance ensures that the money collected is utilized in
a manner that benefits citizens of the country.
4. Other important
sectors are infrastructure development, transport, housing, etc.
(i) Apart from social projects, governments also use money collected
from taxes to fund sectors that are crucial for the wellbeing of their citizens
such as security, scientific research, environmental protection, etc.
(ii) Some of the money is also channeled to fund projects such as
pensions, unemployment benefits, childcare, etc.
4. Explain the direct
and indirect tax with examples.
Answer: Direct Tax:
(i) A Direct tax is the tax whose burden is directly borne by the
person on whom it is imposed, i.e., its burden cannot be shifted to others.
(ii) It is deducted at source from the income of a person who is
taxed.
(iii) Income tax is a direct tax because the person, whose income is
taxed, is liable to pay the tax directly to the Government and bear the burden
of the tax himself. Eg. Corporation tax, wealth tax gift tax estate dirty.
Indirect Tax:
(i) On the other hand when liability to pay a tax is on one person
and the burden of that tax shifts on some other person, this type of tax is
called an indirect tax.
(ii) Indirect Tax is a tax whose burden can be shifted to others.
(iii) For example: Service tax, Sales tax, Excise duty, Entertainment
tax.
5. Why need for tax on
people welfare? And explain it.
Answer: (i) The levying of taxes aims to raise revenue to fund governing or
to alter prices in order to affect demand.
(ii) Some of these include expenditures on economic infrastructure
like, transportation, sanitation, public safety, education, health-care
systems, etc., military, scientific research, culture and the arts, public
works, public insurance, etc. and the operation of government itself.
(iii) When expenditures exceed tax revenue, a government accumulates
debt. A portion of taxes may be used to service past debts.
(iv) Governments also use taxes to fund welfare and public services.
These services can include education systems, pensions for the elderly,
unemployment benefits, and public transportation.
(v) Energy, water and waste management systems are also common
public utilities.
(vi) The purpose of taxation is to maintain the stability of the
currency, express public policy regarding the distribution of wealth,
subsidizing certain industries or population groups or isolating the costs of
certain benefits, such as highways or social security.
(iii) Canon of
Convenience: Taxes should be levied and
collected in such a manner that provides a maximum of convenience to the
taxpayers should always keep in view that the taxpayers suffer the least
inconvenience in payment of the tax.
(iv) Canon of
Economy: Minimum possible money should be spent in the
collection of taxes. Collected amount should be deposited in the Government
treasury.
VIII. Activity
and Project
1. Students are asked
to go to the nearest departmental store and know about the Goods and Service
tax (GST). Teacher and students are discussed about the GST.
2. Teacher asks the
student to write an essay on what is tax? why we pay tax? And how does the
Government use this tax for the welfare of the people.
IX. Life
Skills :
1. Teacher and Students
together discuss about the tax and their importance of development of country.
Related Topics