Equality | Term 1 Unit 1 | Civics | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 1 : Equality
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 1 : Equality
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
answer
1.
Which one of the following does not come under Equality?
a. Non discrimination on the basis of
birth, caste, religion, race, colour, gender.
b. Right to contest in the election.
c. All are treated equal in the eyes of
law.
d. Showing inequality between rich and
poor.
Answer: d) Showing inequality
between rich and poor.
2.
Which one of the following is comes under political Equality?
a. Right to petition the government and
criticize public policy.
b. Removal of inequality based on race,
colour, sex and caste.
c. All are equal before the law.
d. Prevention of concentration of
wealth in the hands of law.
Answer: a. Right to petition the
government and criticize public policy.
3.
In India, right to vote is given to all the citizens at the age of ____________
a. 21
b. 18
c. 25
d. 31
Answer: b. 18
4.
Inequality created by man on the basis of caste, money, religion etc is called
as____
a. Natural inequality
b. Manmade inequality
c. Economic inequality
d. Gender inequality
Answer: b. Manmade inequality
5.
In Switzerland, the right to vote is given to women in the year
a. 1981
b. 1971
c. 1991
d. 1961
Answer: b. 1971
II. Fill in the blanks
1. Civil equality implies equality of
all before law.
2. The Indian constitution deals about
the Right to equality from Article 14 to 18.
3. Right to contest in the election is
a Political Right.
4. Equality means, absent of Social privileges.
III. Give short answer
1.
What is Equality?
Equality is ensuring individuals or groups that are not treated
differently or less favourably on the basis of specific protected
characteristic, including areas of race, gender, disability, religion or
belief, sexual orientation and age.
2.
Why is gender Equality needed?
Gender Equality is the equal right of both men and women to have
access to opportunities and resources.
3.
What is civil Equality?
Civil equality is enjoyment of civil rights by all citizen.
There should not be any discrimination of superior or inferior, the rich or the
poor, caste or creed. Equal rights should be available to all the persons and
nobody should be denied enjoyment of any rights.
IV. Answer in detail
1.
Write about the importance of Equality.
Equality is a powerful moral and political ideal that has
inspired and guided human society for many centuries. The concept of equality
invokes the idea that all human beings have equal worth regardless of their
caste, colour, gender, race or nationality. The democratic ideals such as
liberty, equality etc are meaningful and effective only when they are
implemented with justice.
Social equality means that all citizens are entitled to enjoy
equal status in society. There should not be any discrimination of caste, creed,
colour and race. All should have equal opportunity to develop their personality
and to complete goals.
2.
What is political Equality?
All the democratic countries including India have guaranteed the
political rights to all citizens. It includes
❖ Right to
vote
❖ Right to
hold public office
❖ Right to criticise the government
Citizens should have equal opportunity to actively participate
in the political life. These rights can be enjoyed through the Universal Adult
Franchise. In India the voting right is given to all the citizens who have
attained 18 years of age without any discriminations. India is the first
country to give right to vote to women from the very first general election
held in the year 1952. In Switzerland the right to vote was given to women in
1971. Any person who has completed the age of 25 years can contest in the
election. Right to criticise the government is also very important right and
the people can express their resentment through demonstrations. The value of
the vote of the Prime Minister and value of vote of common man in general
election is same which denotes political equality.
3.
How does the Constitution of India protect the Right to Equality?
Almost the constitutions all the countries in the world have
guaranteed equality. Likewise, the constitution of India has also guaranteed
equality to all citizens by providing Articles form 14-18.
Article 14 - guarantees to all the people equality before law.
Article 15 - deals with
the prohibition of discrimination.
Article 16 - provides equality of opportunity in matters
relating to employment.
Article 17 - abolishes the practice of untouchability.
Article 18 - abolishes the titles conferred to citizen.
Equality before law and equal protection of law have been
further strengthened in the Indian constitution under Article-21.
We can promote e mality by
❖ Treating all fairly.
❖ Creating an
inclusive culture.
❖ Ensuring
equal access to opportunities.
❖ Enabling to
develop full potential.
❖ Making laws
and policies.
❖ Education.
India is a the largest democratic country in the world. Equality
and justice are the pillars of democracy. Justice can be achieved when people
are treated equality. Equality is so important because it preserves the dignity
of an individual. Equality is an important principle for a society to function.
HOTs
How
can we eliminate inequality at school level?
I. Life Skills
Write the correct answer.
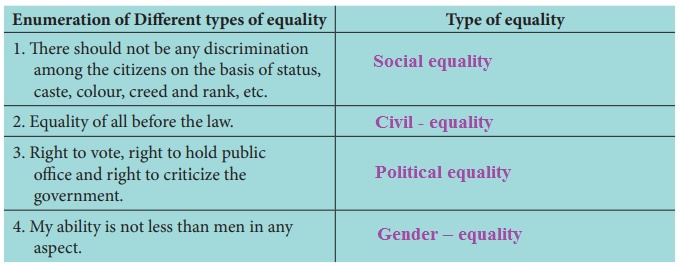
Enumeration of
Different types of equality :
1. There should not be any discrimination among the citizens on
the basis of status, caste, colour, creed and rank, etc. Type of equality: Social equality
2. Equality of all before the law. Type of equality: Civil - equality
3. Right to vote, right to hold public office and right to
criticize the govemement. Type of
equality: Political equality
4. My ability is not less than men in any aspect. Type of equality: Gender – equality
Related Topics