Interior of the Earth | Term 1 Unit 1 | Geography | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 1 : Interior of the Earth
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 1 : Interior of the Earth
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
answer
1.
Nife is made up of ___________ .
a. Nickel and ferrous
b. Silica and aluminum
c. Silica and magnesium
d. Iron and magnesium
Answer: a. Nickel
and ferrous
2.
Earthquake and volcanic eruption occur near the edges of ______________.
a. Mountain
b. Plains
c. Plates
d. Plateaus
Answer: c. Plates
3.
The magnitude of an earthquake is measured by ______________.
a. Seismograph
b. Richter scale
c. Ammeter
d. Rotameter
Answer: b. Richter
scale
4.
The narrow pipe through which magma flow out is called a ______________.
a. Vent
b. Crater
c. Focus
d. Caldera
Answer: a. Vent
5.
Lava cones are _____________
a. mountains of accumulation
b. mountains of deformation
c. relicit mountains
d. fold mountains
Answer: a. mountains of accumulation
6.
The top of the cone of a volcanic moun-tain has a depression known as the ___________
a. crater
b. lopith
c. caldera
d. sill
Answer: a. crater
7.
__________ belt is known as the “Ring of Fire”.
a. Pacific
b. Atlantic
c. Arctic
d. Antarctic
Answer: a. Pacific
II. Fill in the blanks
1) The core is separated from the
mantle by a boundary called Weichart Gutenberg.
2) The earthquake waves are recorded by
an instrument known as Seismograph.
3) Magma rises to the surface and
spreads over a vast area is known as Fissure eruption.
4) An example for active volcano Mt. Stramboli.
5) Seismology is the study of earthquakes.
III. Circle the odd one
1) crust, magma, core, mantle
2) focus, epicenter, vent, seismic waves
3) Uttar Kashi, Chamoli, Koyna, Krakatoa
4) lava, caldera, silica, crater
5) Stromboli, Helens, Hawaii, Fujiyama
Answer: 1) magma 2) vent 3)
Krakatoa 4) silica 5) Fujiyama
IV. Match the following
1) Earth quake - Japanese term
2) Sima - Africa
3) Pacific Ring of Fire- Sudden
movement
4) Tsunami - Silica and magnesium
5) Mt. Kenya - World volcanoes
Answer: 1) Sudden
movement 2) Silica and magnesium 3)
World volcanoes 4) Japanese term 5) Africa
1) Earthquake : Sudden
movement
2) Sima : Silica and
magnesium
3) Pacific Ring of Fire : World
volcanoes
4) Tsunami : Japanese
term
5) Mt. Kenya : Africa
V. Consider the following
statement and (✔)
Tick the appropriate
answer
1. Assertion
(A): There structure of the earth may be compared to that of anApple.
Reason
(R): The interior of the earth con-sists of
crust, mantle and core.
a. A and R are correct and A explains R
b. A and R are correct but A does not
explain R
c. A is incorrect but R is correct
d. Both A and R are incorrect
Answer: a. A and R are correct
and A explains R
2. Assertion
(A): The Pacific Ocean includes two thirds of the world’s volcanoes.
Reason
(R): The boundary along the
Eastern and Western coast areas of the Pacific Ocean is known as the Pacific
Ring of Fire.
a. A and R are correct and A explains R
b. A and R are correct but A does not
explain R
c. A is incorrect but R is correct
d. Both A and R are incorrect
Answer: b. A and R
are correct but A does not explain R
VI. Answer in a word
1.
Name the outer most layer of the earth.
The crust.
2.
What is SIAL?
The crust comprises two distinct parts. The upper part consists
of granite rocks and forms the continents. It has the main mineral constituents
of silica and alumina. So it is collectively referred to as Sial.
3.
Name the movement of the Earth’s lithospheric plates?
Tectonic movement.
4.
Give an example of extinct volcano
Kilimanjaro
VII. Answer the following
briefly
1.
What is mantle?
The second layer of the earth beneath the crust is called the
mantle. It is separated from the crust by a boundary called Mohorovicic
discontinuity.
2.
Write note on the core of the earth?
The innermost layer of the earth is called the core. It is also
known as barysphere. It is separated from the mantle by a boundary called
Weichart-Gutenberg discontinuity.
3.
Define Earthquake?
A sudden movement of a portion of the earth's crust which
produces a shaking or trembling is known as an earthquake.
4.
What is a Seismograph?
The earthquake waves are recorded by an instrument known as
seismograph.
5.
What is a volcano?
A volcano is a vent or an opening in the earth's crust through
which hot magma erupts from deep below the surface.
6.
Name the three types of volcanoes based on shape.
On the basis of shape, there are three types of volcanoes. They
are:
1. Shield volcano
2. Cinder-cone volcano
3. Composite volcano
VIII. Give reason
1.
No one has been able to take samples from the interior of the earth
Due to high temperature of heat in the interior of the earth it
is impossible to take samples from the interior.
2.
The Continent crust is less dense than the oceanic crust
The continental crust is less dense than the oceanic crust
because it is made of both light and dense rock types. The oceanic crust is
composed mostly of dense rocks such as basalt.
IX. Distinguish between
1.
SIAL and SIMA
SIAL and SIMA
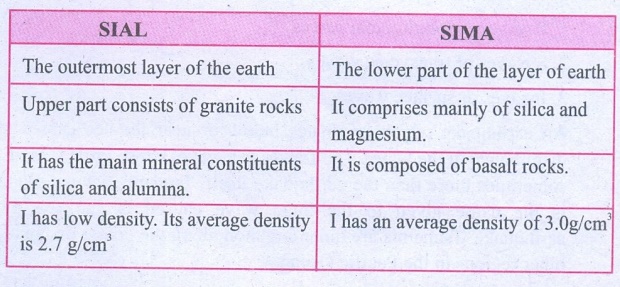
SIAL
The outermost layer of the earth
Upper part consists of granite rocks
It has the main mineral constituents of silica and alumina.
I has low density. Its average density is 2.7 g/cm3
SIMA
The lower part of the layer of earth
It comprises mainly of silica and magnesium.
It is composed of basalt rocks.
I has an average density of 3.0g/cm3
2.
Shield volcano and composite volcano
3.
Active volcano and dormant volcano

Active volcano
Volcanoes that erupt frequently are called active volcanoes.
Most of the active volcanoes lie in the Pacific Ring of Fire
belt which lies along the Pacific Coast.
Dormant volcano
Dormant volcanoes have shown no sign of activity for many years
but they may become active any time.
Mt Fujiyama in Japan and Mt Krakatoa of Indonesia are examples
of this types.
X. Answer the following
questions in detail
1.
Write about the effects of an earthquake?
Earthquakes may cause changes in the earth's surface. Vibrations
often set landslides in mountains regions. A greater danger in an earthquake is
the falling of buildings. Most of the houses which collapsed were made of mud
and bricks and proved to be death traps. Fire is another great danger.
Underground water system is naturally disturbed by such movements.
There are three types of earthquake waves:
1. P waves or longitudinal waves.
2. S waves or transverse waves.
3. I waves or surface waves.
An earthquake which originates below or near the sea causes
great disturbance in the water. The floods and waves cause great loss of life,
sometimes more than the earthquake itself. Tsunami, a Japanese term, is the
name given to the huge wave caused in the sea by an earthquake. Tsunamis are
quite common along the coasts of Japan and other regions in the Pacific Ocean.
2.
Describe the classification of volcanoes based on the eruptions.
The shape of a volcano depends on the type of lava and the force
of the eruption. On the basis of shape, there are three types of volcanoes.
They are:
1. Shield volcano
2. Cinder-cone volcano
3. Composite volcano
1. Shield volcano : A shield volcano is formed by quiet eruption of lava with a low
silica content. Such a volcano has a wide base and a cone with gentle slopes.
Volcanoes of the Hawaii islands are of this type.
2. Cinder-cone
volcano: Silica-rich magma traps gases inside the
volcano until enough pressure is built to push the magma out of the earth's
crust. When this type of volcano erupts, it shoots gases, ash, etc. with great
force throwing them several kilometres up into the atmosphere. Such volcanoes
have steep slopes and are made of cinder and ash. They are known as cinder-cone
volcanoes. Many volcanoes of Mexico and Central America belong to this group.
3. Composite
volcano: Composite volcanoes are made of alternate
layers of lava, cinder and ash. They are also called strato volcano. St. Helens
is an example of composite volcano.
3.
Name the major zones of volcanic activity and explain any one.
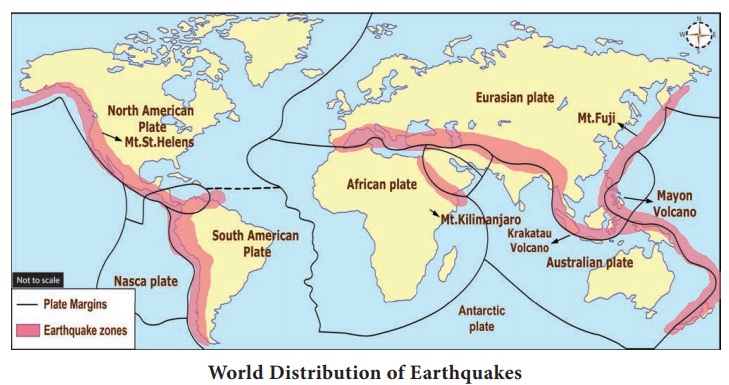
There are three major zones of volcanic activities in the world.
They are:
1. The Circum - Pacific belt
2. The Mid continental belt
3. The Mid Atlantic belt
1. Circum Belt
This is the volcanic zone of the convergent oceanic plate
boundary. It includes the volcanoes of the eastern and western coastal areas of
Pacific Ocean. This zone is popularly termed as the Pacific Ring of Fire which
has been estimated to include two- thirds of the world's volcanoes.
2. Mid continental
belt
This is the volcanic zone of convergent continental plate
boundaries that includes the volcanoes of Alpine mountain chains, the
Mediterranean Sea and the fault zone of eastern Africa. The important volcanoes
are Vesuvius, Stromboli, Etna, Kilimanjaro and Kenya. Surprisingly, the Himalayas
have no active volcanoes at all.
3. Mid Atlantic
Belt
This belt represents the divergent boundary of plates located
along the mid-Atlantic ridges. Volcanoes of this area are mainly of fissure
eruption type. Iceland is the most active volcanic area and is located on the
mid-Atlantic ridge. St. Helena and Azores Island are other examples.
XI. HOTs
1.
The earth’s interior is very hot. Why?
The Earth's interior is very hot. It is due to two main reasons.
- the heat from when planet form.
- The heat from the decay of radio active elements.
2.
Are Volcones Destructive (or) Constructive?
They are destructive because they can destroy anything in the
lava's way. When they erupt they cause damage by tearing down buildings with
lava and black smoke with force. The ashfall makes people unable to breathe. It
obstructs visibility during the flight by aeroplanes.
They result in construction of new land forms.
3.
How does volcaone make on Island?
Volcanic Islands are formed by volcanic activity on the sea bed,
often near the boundaries of the tectonic plates that form earth's curst. Where
two plates pull apart, lava erupts to form an undersea ridge. Layers of lava
built up until a ridge breaks the sea's surface to form an island. Sometimes a
whole chain of volcanic islands called an Island arc is formed in this way.
Some island arcs contain thousands of islands.
XII. Activity
1.
On an outline map of the world, mark the Pacific Ring of Fire
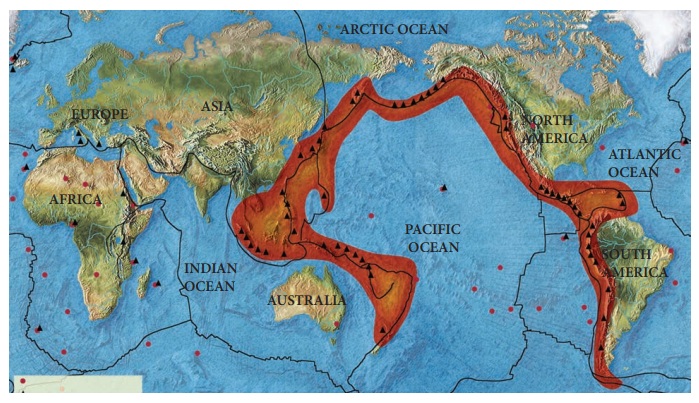
2.
Label the parts of volcano.
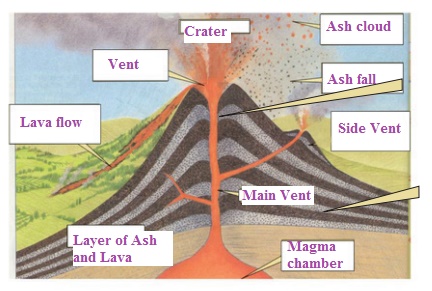
3.
Prepare an album on earthquake and volcanoes.
PUZZLE
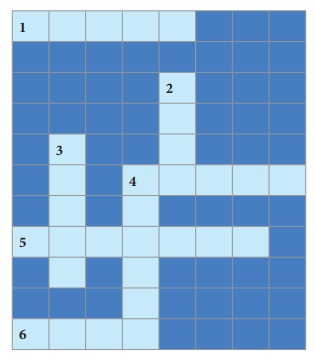
Across
1.
Point of origin of Earthquake
4.
Molten rock under the surface
5.
Waves triggered by deep ocean earthquake
6.
Inner layer of the Earth
Down
2.
Extinct volcano in Europe
3.
Top layer of the Earth
4. Middle layer of Earth
WORLD MAP

LABEL THE PARTS OF VOLCANO

Related Topics