Book Back Important Questions Answers | Choose the Correct Answers | Short, brief Answers | Zoology - Applications of biotechnology: Questions and Answers (Evaluation) | 12th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Applications of biotechnology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Applications of biotechnology
Applications of biotechnology: Questions and Answers (Evaluation)
Evaluation
1. The first clinical gene therapy was done for the treatment of
a) AIDS
c) Cancer
d) Cystic fibrosis
e) SCID
Answer: c) Cystic
fibrosis
2. Dolly, the sheep was obtained by a technique known as
a) Cloning by gene transfer
b) Cloning without the help of gametes
c) Cloning by tissue culture of somatic cells
d) Cloning by nuclear transfer
Answer: d) Cloning by
nuclear transfer
3. The genetic defect adenosine deaminase deficiency may be cured permanently by
a) Enzyme replacement therapy
b) periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes having ADA cDNA
c) administering adenosine deaminase activators
d) introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into embryo at an early stage of development.
Answer: a) Enzyme
replacement therapy
0. GEAC stands for
a) Genome Engineering Action Committee
b) Ground Environment Action Committee
c) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee
d) Genetic and Environment Approval Committee
4. How many amino acids are arranged in the two chains of Insulin?
a) Chain A has 12 and Chain B has 13
b) Chain A has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
c) Chain A has 20 and chain B has 30 amino acids
d) Chain A has 12 and chain B has 20 amino acids.
Answer: b) Chain A
has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
5. PCR proceeds in three distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of
a) Denaturation, Annealing, Synthesis
b) Synthesis, Annealing, Denaturation
c) Annealing, Synthesis, Denaturation
d) Denaturation, Synthesis, Annealing
Answer: a)
Denaturation, Annealing, Synthesis
6. Which one of the following statements is true regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
b) It serves as a selectable marker
c) It is isolated from a Virus
d) It remains active at a high temperature.
Answer: d) It remains
active at a high temperature
7. ELISA is mainly used for
a) Detection of mutations
b) Detection of pathogens
c) Selecting animals having desired traits
d) Selecting plants having desired traits
Answer: b) Detection
of pathogens
8. Transgenic animals are those which have
a) Foreign DNA in some of their cells
b) Foreign DNA in all their cells
c) Foreign RNA in some of their cells
d) Foreign RNA in all their cells
Answer: b) Foreign
DNA in all their cells
9. Recombinant Factor VIII is produced in the ________ cells of the Chinese Hamster
a) Liver cells
b) blood cells
c) ovarian cells
d) brain cells.
Answer: c) ovarian
cells
10.Vaccines that use components of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called
a) Subunit recombinant vaccines
b) attenuated recombinant vaccines
c) DNA vaccines
d) conventional vaccines.
Answer: a) Subunit
recombinant vaccines
11. Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of PCR. Write the role of primers and DNA polymerase in PCR. Name the source organism of the DNA polymerase used in PCR.
• Number of primers
required for each cycle of PCR is 2. They are forward and reverse primers.
• Primer : A primer is a short strand of RNA or DNA that serves as
starting point for DNA synthesis.
• DNA poymerase : The DNA polymerase used in PCR is Taq polymerase. This
enzyme is able to withstand the high temperature and makes the new strands of
DNA using existing strands as templates.
• DNA polymerase : Taq polymerase is obtained from thermophilic bacterium
Thermus aquaticus.
12. How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using PCR?
• DNA is heated to
separate two strands this is called deneturation. It is done at 95° C
• Primer is added and
temperature is reduced to 75° C. This is called anneling. This will allow Taq
polymerase to extend each primer.
• Free nucleotides are
added along with DNA polymerase.
• The new strand of each
double stranded DNA (genes) extends to a variable distance downstream.
13. What is genetically engineered Insulin?
• The insulin which are
obtained from recombinant DNA technology are called genetically engineered
Insulin.
• The approval to use
recombinant insulin for diabetes mellitus was given in 1982.
• This is also called
humulin.
14. Explain how “Rosie” is different from a normal cow.
• Rosie is a transgenic
cow.
• It was considered
different from a normal cow as it produced human protein enriched milk.
• The milk contained
human alpha - lactalbumin
• It was a nutritionally
a more balanced product for human babies than normal cow.
15. How was Insulin obtained before the advent of rDNA technology? What were the problems encountered?
• In the early years,
insulin isolated and purified from the pancreas of pigs and cows.
• It was used to treat
diabetic patients
Problem of using animal insulin
• It resulted in the
occurrence of allergic reaction in some diabetic patients due to minor
variation in their structure.
16. ELISA is a technique based on the principles of antigen-antibody reactions. Can this technique be used in the molecular diagnosis of a genetic disorder such as Phenylketonuria?
• Yes, phenylketonuria
can be diagnosed by ELISA
• ELISA test used
antibodies against phenylalanine which are then bound by another antibody which
binds the original antibody as an antigen.
17. Gene therapy is an attempt to correct a Genetic defect by providing a normal gene into the individual. By this the function can be restored. An alternate method would be to provide gene product known as enzyme replacement therapy, which would also restore the function. Which in your opinion is a better option? Give reasons for your answer.
• Gene therapy is better
than the enzyme replacement therapy.
• Because gene therapy
permanently cure the genetic disease caused by single gene mutation.
• But enzyme replacement
therapy manage the disease and their benefit is temporary.
18. What are transgenic animals? Give examples.
Animals that are
produced by DNA manipulations are called transgenic animals or genetically
engineered or genetically modified organisms.
Example: Transgenic mice, rat, rabbit, pig, cow, sheep and fish
etc.
19. If a person thinks he is infected with HIV, due to unprotected sex, and goes for a blood test. Do you think a test such as ELISA will help? If so why? If not, why?
• Yes, ELISA is used to
diagnose AIDS.
• ELISA is a tool for
determining serum antibody concentrations.
• It is also used for
detecting the presence of specific antigens and hormones such as human
chorionic gonadotropins.
20. Explain how ADA deficiency can be corrected?
It can be corrected by
1) Bone marrow transplantation:
• In some children ADA
deficiency could be cured by bone marrow transplantation.
• Defective immune cells
could be replaced with healthy immune cells from a donor.
• In some patients it
can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy in which functional ADA is
injected into the patient.
2) Gene therapy :
• The lymphocytes from
the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium.
• The functional ADA
cDNA encoding this enzyme is introduced into the lymphocytes using retrovirus.
• These genetically
engineered lymphocytes are subsequently returned to the patient.
• The disease could be
cured permanently if the ADA gene is introduced into the bonemarrow cells of
early embryo.
21. What are DNA vaccines?
• DNA vaccine consists
of a gene encoding an antigenic protein
• It is inserted into a
plasmid and then incorporated into the cells in a target animal.
• DNA instructs the
cells to make antigenic molecules which are displayed on its surfaces.
• This would evoke an
antibody response to the free floating antigen secreted by the cells.
22. Differentiate between Somatic cell gene therapy and germline gene therapy.
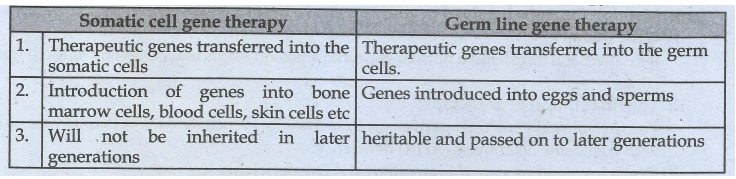
Somatic cell gene
therapy
1. Therapeutic genes
transferred into the somatic cells
2. Introduction of
genes into bone marrow cells, blood cells, skin cells etc
3. Will not be
inherited in later generations
Germ line gene therapy
1. Therapeutic genes
transferred into the germ cells.
2. Genes introduced
into eggs and sperms
3. heritable and
passed on to later generations
Five Mark Questions
23. What are stem cells? Explain its role in the field of medicine.
Stem Cells:
Stem cells are
undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals. These cells
maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic
divisions.
Role in the field of medicine :
i) Stem cells research
has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to
regenerate damaged and diseased organs.
ii) Stem cells are
capable of self renewal and exhibit cellular potency
iii) Stem cells can
differentiate into all types of cells that are derived from any of the three
germ layers ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
iv) In mammals there
are two main types of stem cells -enbryonic stem cells (ES cells) and adult
stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells :
v) ES cells are
pluripotent and can produced the three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm
and endoderm.
vi) Embryonic stem
cells are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a number of types
of cells.
ES cells are isolated
from the epiblast tissue of the inner cell mass of a blastocyst.
When stimulated ES can
develop into more than 200 cell types of the adult body.
ES cells are immortal.
Adult stem cells:
vii) Adult stem cells
are found in various tissues of children as well as adults.
An adult stem cell or
somatic stem cell can divide and create another cell similar to it. Most of the
adult stem cells are multipotent and can act as a repair system of the body, replenishing
adult tissues.
The red bone marrow is
a rich source of adult stem cells.
viii) The most
important and potential application of human stem cells is the generation of
cells and tissues that could be used for cell based therapies.
Human stem cells could
be used to test new drugs.
24. One of the applications of biotechnology is ‘gene therapy” to treat a person born with a hereditary disease.
i. What does “gene therapy” mean?
ii. Name the hereditary disease for which the first clinical gene therapy was used.
iii. Mention the steps involved in gene therapy to treat this disease.
i) Gene therapy :
It involves the
transfer of a normal gene into a person's cells that caries one or more mutant
alleles.
ii) The first clinical gene therapy :
The first clinical
gene therapy was given in 1990 by French Anderson to four year old girl with
adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
iii) Steps involved in gene therapy to treat ADA deficiency
:
• Bacterium carrying
plasmid with cloned normal human ADA gene is selected.
• Genetically disabled
retrovirus is selected.
• Cloned ADA gene is
incorporated into virus.
• Retrovirus infects T
cells and Transfer of ADA gene into cells.
• Cells are grown in
culture to ensure ADA gene is active.
• Genetically altered
cells are reimplanted to produce ADA.
25. PCR is a useful tool for early diagnosis of an Infectious disease. Elaborate.
• The specificity and
sensitivity of PCR is useful for the diagnosis and treatment of viral and
bacterial diseases.
• The concept behind PCR
based diagnosis of infectious disease is simple. If the pathogen is present in
clinical specimen, it's DNA will be present.
• It's DNA has unique
sequences that can be detected by PCR. Often using clinical specimens in the
PCR mixture.
• PCR is a valuable tool
for diagnosis and monitoring retroviral intentions like tuberculosis.
• Several virally
induced cancers like cervical cancer caused by papilla virus also can be
detected by PCR.
26. What are recombinant vaccines?. Explain the types.
Recombinant vaccines :
The recombinant
vaccines are generally of uniform quality and produce less side effects as
compared to the vaccines produced by conventional methods.
Different types of
recombinant vaccines include subunit recombinant vaccines attenuated
recombinant vaccines and DNA vaccines.
i) Subunit recombinant vaccines
• Vaccines that use
component of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called
sub unit vaccines; recombinant DNA technology is very suited for developing new
subunit vaccines.
• It includes components
like proteins, peptides and DNAs of pathogenic organisms.
• The advantages of
these vaccines include their purity in preparation, stability and safe use.
ii) Attenuated recombinant vaccines
• This includes
genetically modified pathogenic organisms that are made non pathogenic and are
used as vaccines.
• It is now possible to
genetically engineer the organisms (bacteria or viruses) and use them as live
vaccines and such vaccines are reffered as attenuated recombinant vaccines.
27. Explain why cloning of Dolly, the sheep was such a major scientific breakthrough?
• Dolly, a Finn Dorset
sheep, was bom on July 5th 1996 at Roslin Institute of Edinburgh Scotland.
• It was developed by
nuclear transfer.
• It is considered as
one of the most significant scientific breakthrough ever.
• Dolly's birth and
subsequent survival proved that adult cells can regrow themselves into a new
being.
• This knowledge changed
what scientists thought was possible and opened up a lot of possibilities in
biology and medicine.
28. Mention the advantages and disadvantages of cloning.
Advantages :
i) Offers benefits for
clinical trials and medical research. It can help in the production of proteins
and drugs is the field of medicine.
ii) It helps stem cell
research
iii) Animal cloning
could help to save endangered species.
Disadvantages :
i) Animal and human
activists see it as a threat is biodiversity which will have as impact on
populations and the ecosystem.
ii) The process is
tedious and very expensive
iii) It can cause
animals to suffer.
iv) Surrogates were
manifesting adverse out comes. Cloned animals have high mortality rate.
v) It might compromise
human health through consumption of cloned animal meat.
vi) Cloned animals
aged faster than normal animals and are less healthy than the parent organisms
as discovered in Dolly.
vii) Cloning can lead
to occurrence of genetic disorders in animals.
viii) More than 90% of
cloning attempts fail-to produce a viable offspring.
29. Explain how recombinant Insulin can be produced.
• The donor DNA (Insulin
producing gene) is obtained from human pancreatic cells.
• A vector called
plasmid is isolated and cut into fragments by using restriction endonuclease
enzyme.
• Donor and plasmid DNA
is joined together by ligase enzyme as a result recombinant DNA is obtained.
• Recombinant DNA is
introduced into a suitable bacterium. Now this is called as recombinant
bacterium.
• Recombinant bacteria
multiplying and producing human insulin in fermentation tank.
• From the fermentation
tank insulin is extracted and purified.
30. Explain the steps involved in the production of recombinant hGH.
i) human growth
hormones somatostatin and somatotropin are peptide homones secreted by the
pituitary gland.
ii) Deficiency of
human growth hormone causes dwarfism, which could be treated by injecting hGH
extracted from the human pituitary glands.
iii) The gene for hGH
is isolated from the human pituitary gland cells. The isolated gene is inserted
into a plasmid vector and then is transferred into E.coli.
iv) The recombinant
E.coli then starts producing human growth hormone. The recombinant E.coli are
isolated from the culture and mass production of hGH is carried out by
fermentation technology.
v) A recombinant form
of human growth hormone called somatropin is used as a drug to treat growth
disorders in children.
Extra One mark Questions and Answers
1. Genetic engineering has been successfully used for producing
a) Transgenic mice for testing safety of polio vaccine before used in humans.
b) Transgenic models for studying new treatments for certain cardiac diseases.
c) Transgenic cow Rosie which produces high fat milk for making ghee.
d) Animals like bulls for farm work as they have super power.
2. Some of the characteristics of Bt cotton are
a) Long fibre and resistance to aphids
b) Medium yield, long fibre and resistance to beetle pests.
c) High yields and production of toxic protein crystals which kill dipteran pests.
d) High yield and resistance to bollworms
3. Bacillus thuringiensis forms protein crystals which contain insecticidal protein. This protein
a) Binds with epithelia cells of midgut of the insect pest ultimately killing it.
b) Is coded by several genes including the gene cry.
c) Is activated by acid pH of the foregut of the insect pest.
d) Does not kill the carrier bacterium which is itself resistant to this toxin.
4. Read the following four statements (A to D) about certain mistakes in two of them.
A) The first transgenic buffalo, Rosie produced milk which was human alpha – lactalbumin enriched.
B) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
C) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology
D) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in transfer of rDNA into the host.
Which of the two statements have mistakes?
a) B and C
b) C and D
c) A and C
d) A and B
5. The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of
a) Non-recombinant bacteria containing β-galactosidase.
b) Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria.
c) Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria.
d) Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
6. Which body of the Government of India regulates GM research and safety of introducing GM organism for public services?
a) Bio-safety committee
b) Indian council of agricultural research
c) Genetic engineering approval committee
d) Research committee on Genetic manipulation
7. In genetic engineering, a DNS segment (gene) of interest is transferred to the host cell through a vector. Consider the following four agents (A to D) in this regard and select correct option about which one or more of these can be used as vector/vectors.
A) A bacterium B) Plasmid
C) Plasmodium D) Bacteriophage
a) (A), (B) and (D) only
b) (A) only
c) (A) and (C) only
d) (B) and (D) only
8. Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?
a) 5’ – CGTTCG – 3’ 3’ –ATGGTA -5’
b) 5’-GATATG -3’ 3’ CTACTA -5’
c) 5’ –GAATTC – 3’ 3’ – CTTAAG-5’
d) 5’ –CACGTA -3’ 3’ –CTCAGT -5’
9. Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which
a) Make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule.
b) Recognize a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase.
c) Restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
d) Remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule.
10. Stirred – tank bioreactors have been designed for
a) Addition of preservatives of the product
b) Purification of the product
c) Ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
d) Availability of oxygen throughout the process
11. There is a retriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does ‘co’ part in it stand for?
a) Coelom
b) Coenzyme
c) Coli
d) Colon
12. Which one is true state regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells.
b) It serves as selectable marker
c) It is isolated from a virus.
d) It remains active at high temperature.
13. For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
a) Silver or Platinum
b) Platinum or Zinc
c) Silicon or Platinum
d) Gold or Tungsten
Related Topics