Trends in Economic Zoology | Zoology - Answer the following questions | 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Answer the following questions
Trends in Economic Zoology
Evaluation
Answer the following questions
13. Animal husbandry is the science of rearing, feeding and caring, breeding and disease control of animals. It ensures supply of proper nutrition to our growing population through activities like increased production and improvement of animal products like milk, eggs, meat, honey, etc.
a. Poultry production depends upon the photoperiod.Discuss
b. Polyculture of fishes is of great importance.
a)
Poultry production depends upon the photoperiod:
1. The photoperiod
stimulates the growth and breeding of birds.
2. It increases
the life span of birds
3. As it increases
the metabolic rate the egg laying fowls will lay more eggs.
4. The light induces
the endocrine glands and increases hormone secretion.
5. The light intensity
depends on its wavelengths.
b)
Poly culture of fishes is of great importance:
1. In poly culture
fishes will not fitht for food.
2. No deficiency
of oxygen.
3.
In this culture the upper layer fishes feeds on phy to and zoo planktons the middle
layer fishes feeds on submerged plants and fishes lives in the deeper layers feeds
on bottom dwellers debris of plants and animals.
4.
In poly culture the fishes use the maximum food to convert it into meat.
5.
Fishes have high growth rate in short periods.
Eg.:
Catlacatla, cirrhinus mrigla labeorohita are cultured through polyculture.
15. Write the advantages of vermicomposting.
1.
Vermicompost is rich in essential plant nutrients.
2.
It improves soil structure texture aeration and water holding capacity and prevents
soil erosion.
3.
Vermicompost is a rich nutrients.
4.
Used as a manure for terrace gardening.
5.
It enhances seed germination and ensures good plant growth.
16. Name the three castes in a honey bee colony
1.
Queen bee
2.Drone
3.
Worker bee
17. Name the following
i. The largest bee in the colony
ii. The kind of flight which the new virgin queen takes along with the drones out of the hive
1.
The largest bee in the colony - Queen bee
2.
The kind of flight which the new virgin queen takes along with the drones out of
the hive - Nuptial flight
18. What are the main duties of a worker bee?
1.
Secretion of royal jelly
2.
Prepares bee - bread to feed the larvae
3.
Feeds the queen
4.
Takes care of the queen and drones.
5.
Secretes bee wax
6.
Builds combs
7.
Cleans the combs.
8.
Guards the bee hive
9.
Searches and gathers the pollen nectar and propolis and water.
19. What happens to the drones after mating flight?
• The drones are attracted to the pheromones
of queen bee and mating taking place. The drone dies after copulation.
20. Give the economic importance of Silkworm
1.
Silk fibres are utilized in preparing silk clothes.
2.
Silk fibres are combined with natural or synthetic fibres to produce teri - silk,
cot - silk.
3.
Silk is used in industries and for military purposes.
4.
It is used in the manufacturing of fishing fibres, parachutes, cartridge bags insulation
coils for telephone wire less receivers
5.
It is used to manufacture tyres of racing cars, filter fibres, in medical dressing
and as suture materials.
21. What are the Nutritive values of fishes?
1.
Fishes form a rich sources of protein food.
2.
It is a good stable food to tide over the nutritional needs of man.
3.
Fish species such as sardines mackeral, tuna herrings have high amino acid concentrations.
4.
They have histidine which is responsible for the meaty flavor of the flesh.
5.
It is rich in omega 3 fatty acids.
6.
Minerals such as calcium magnesium phosphorus potassium iron manganese iodine and
copper is present in fishes.
22. Give the economic importance of prawn fishery
• Prawn are widely cultured
• They are highly palatable.
• They are rich in glycogen protein
with low fat content.
• Commercially they provide good profit.
23. Give the economic importance of lac insect
• Lac is used as a sealing wax and adhesive
for optical instruments.
• It is a good insulator.
• It is used in the preparations of
shoe and leather polishes and as a protective coating of wood.
• It is used in laminating paper board
photographs, plastic moulded articles.
• Used as a filling material for gold ornaments.
24. Name any two trees on which lac insect grows.
1.
Acacia catechu
2. Acacia nilotica
25. Define cross breeding.
• Breeding between a superior male of
one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross breed progeny have
superior traits.
26. What are the advantages of artificial insemination?
1.
It increases the rate of conception.
2.
It avoids, genital diseases.
3.
Semen can be collected from injured bulls which have desirable traits.
4.
Superior animals located apart can be breed successfully.
27. Discuss the various techniques adopted in cattle breeding?
• Multiple ovulation embryo transfer
technology is a method of propagation of animals with desirable traits.
• This method is applied when the success
rate of crossing is low even after insemination.
• Follicle stimulating hormone is administered
to cows for inducing follicular maturation and super ovulation.
• 6-8 eggs can be produced by this technology.
• The eggs are taken from genetic mother
and fertilized artificially.
• The embryo at 8 - 32 celled stage
are transferred to a surrogate mother.
For
another round of ovulation the same genetic mother is utilized.
• It is used in high milk yielding females
and high quality meat production.
28. Mention the advantages of MOET.
• Advantage of this techonology is to
produce high milk yielding females and high quality meat yielding bulls in a short
time.
29. Write the peculiar characters of duck.
Peculiarity
of Ducks:
1.
The body is fully covered with oily feathers.
2.
They have a layer of fat under their skin which prevents it from getting wet.
3.
They lay eggs at night orin the morning.
4.
The ducks feed on rice bran kitchen wastes waste fish and snails.
30. Explain the life cycle of bombyx mori.
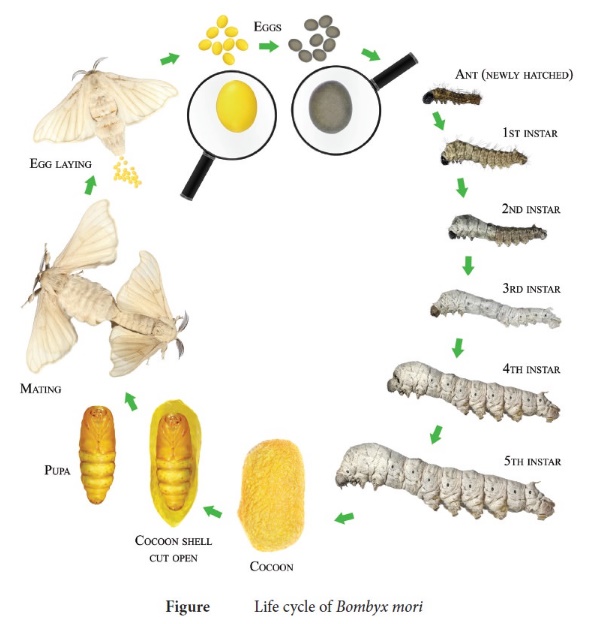
Introduction:
• The adult of Bombyx mori is about 2.5 cm in length and pale creamy white in colour.
• Due to heavy body and feeble wings,
flight is not possible by the female moth.
Egg
laying:
• The female starts egg laying which
is completed in 1-24 hours.
• A single female moth lays 400-500
eggs depending upon the climatic conditions.
Types
of eggs:
1.
Diapause type:
The
diapause type is laid by silkworms inhabiting the temperate regions.
2.
Non-diapause type:
The
silkworms belonging to subtropical regions like India lay non-diapause type of
eggs.
Larva
(or) caterpillar:
• The eggs after ten days of incubation
hatch in to larva called as caterpillar.
• The newly hatched caterpillar is about
3mm in length and is pale, yellowish - white in colour.
• The caterpillar are provided with
well developed mandibulate type of mouth-parts adopted to feed easily on the mulberry
leaves.
Moulting:
• After 1st, 2nd and 3rd and 4th moultings
caterpillars gets transformed into 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th instars respectively (Fig.
12.3)
• It takes about 21 to 25 days after
hatching.
• The fully grown caterpillar is 7.5
cm in length.
Pupa:
• It develops salivary glands, stops
feeding and
undergoes pupation.
• The
caterpillars stop feeding and move towards the corner among the leaves and secretes
a sticky fluid through their silk gland.
• The
secreted fluid comes out through spinneret (a narrow pore situated on the hypopharynx)
and takes the form of long fine thread of silk which hardens on exposure to air
and is wrapped around the body of caterpillar in the forms of covering called as
cocoon.
Cocoon:
• It is
the white coloured bed of the pupa whose outer threads are irregular while the inner
threads are regular.
• The
length of continuous thread secreted by a caterpillar for the formation of cocoon
is about 1000-2000 metres which requires 3 days to complete.
Moth:
• The
pupal period lasts for 10 to 12 days and the pupae cut through the cocoon and emerge
in to adult moth.
• This
moth is unisexual in nature and does not feed during its very short life period
of 2-3 days.
• Just
after emergence, male moth copulates with female for about 2-3 hours and if not
separated, they may die after few hours of copulating with Female.
Related Topics